Back to List
The information contained within this area is intended for use:
- By a Qualified Veterinarian
- Those under instruction of said Veterinarian
- A holder of Scheduled Authority of a Restricted Veterinary Medicine
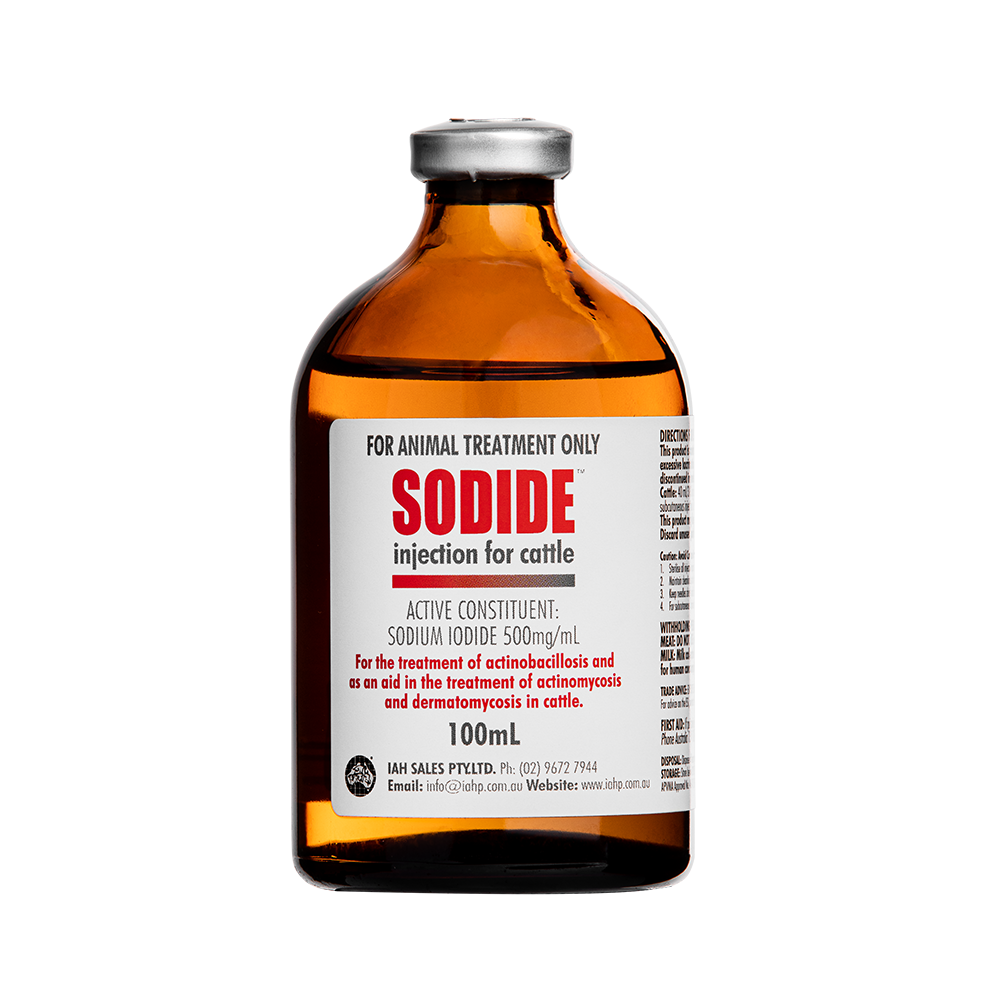
Sodide™
Treats woody tongue in cattle and supports treatment in horses, with added efficacy against lumpy jaw, fungal skin infections, sporotrichosis and granulomatous rhinitis in cattle and horses.
- NEW: Now registered for use in horses
- For the treatment of Actinobacillosis (woody tongue) in cattle and as an aid in treatment of Actinobacillosis in horses.
- It also assists in treating infections caused by Actinomycosis (lumpy jaw), Dermatomycosis (Trichophyton spp.), Sporotrichosis and Granulomatous rhinitis in cattle and horses
- This product may be given only by, or under supervision, of a veterinary surgeon.
Pack sizes: 100ml, 250ml
Available: Australia
More Info & Datasheets
Q. What is sodide used for?
A: For the treatment of Actinobacillosis (woody tongue) in cattle and as an aid in treatment of Actinobacillosis in horses. It also assists in treating infections caused by Actinomycosis (lumpy jaw), Dermatomycosis (Trichophyton spp.), Sporotrichosis and Granulomatous rhinitis in cattle and horses.
Q. What is the difference between lumpy jaw and wooden tongue?
A: Lumpy jaw (Actinomycosis) and Wooden tongue (Actinobacillosis) occur throughout Australia. It can affect cattle of all breeds, age and sex.
Lumpy jaw is caused by infection with the bacterium Actinomyces bovis that enters the body through cuts and abrasions in the mouth. Lumpy jaw produces lumps on the upper and lower jawbones. Symptoms include swelling, the bone becomes enlarged and honeycombed, and full of pus. If left untreated disfiguration of the head can occur and loss of body condition.
Wooden tongue is caused by infection with the bacterium Actinobacillus lignieresii that enters the body through cuts and abrasions in the mouth. The onset of the disease is usually quite rapid. Symptoms include in inflammation of the tongue, which will become hard, swollen, and painful. Usually detected when the tongue is protruding from the mouth with swelling around the lower jawbones. Early treatment of wooden tongue is usually successful, however advanced cases may fail to respond.
Lumpy jaw is caused by infection with the bacterium Actinomyces bovis that enters the body through cuts and abrasions in the mouth. Lumpy jaw produces lumps on the upper and lower jawbones. Symptoms include swelling, the bone becomes enlarged and honeycombed, and full of pus. If left untreated disfiguration of the head can occur and loss of body condition.
Wooden tongue is caused by infection with the bacterium Actinobacillus lignieresii that enters the body through cuts and abrasions in the mouth. The onset of the disease is usually quite rapid. Symptoms include in inflammation of the tongue, which will become hard, swollen, and painful. Usually detected when the tongue is protruding from the mouth with swelling around the lower jawbones. Early treatment of wooden tongue is usually successful, however advanced cases may fail to respond.
Sodide™
Active constituents:
Each mL contains: Sodium Iodide 500mg
For the treatment of Actinobacillosis (woody tongue) in cattle and as an aid in treatment of Actinobacillosis in horses. It also assists in treating infections caused by Actinomycosis (lumpy jaw), Dermatomycosis (Trichophyton spp.), Sporotrichosis and Granulomatous rhinitis in cattle and horses. This product may be given only by, or under supervision, of a veterinary surgeon.






